Anyone pursuing a medical degree is already a committed, hardworking student, but it helps to know what the path ahead might look like and how long it will take to get to your final destination. And while any doctor will tell you to choose a specialty based on your passion and interest, considerations such as medical school cost, family planning, and age at which you’ll finally be earning a salary are good to know in advance.
WONDERING WHERE YOU STAND AS A MEDICAL SCHOOL CANDIDATE?
So how long is medical school? The answer: it depends. Every specialty has its own requirements, but all doctors must pass through several stages to become board-certified, independent physicians. The following will walk you through each step on the med school timeline to give you an idea of exactly how long is med school and when you might finally wear the white coat.
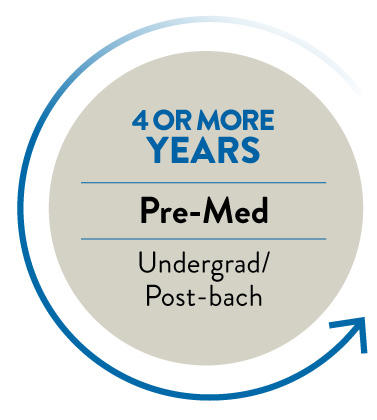
UNDERGRAD: 4 YEARS
You might think that medical school work begins after you graduate college, but it’s actually best to start planning your educational path as soon as you’ve made the decision to become a doctor.
The first hurdle to overcome is the MCAT®, or Medical College Admission Test®, which students typically take in their junior year of college. The test is 7 ½ hours long and requires 200-300 hours of studying, so some students opt to take an MCAT test prep course. There are also practice tests available for purchase via the Association of American Medical Colleges website.
POST-BACCALAUREATE: 1-2 YEARS (OPTIONAL)
The core requirements for med school admissions include a large number of science courses. Students who major in chemistry or biology can knock through some of these requirements during undergrad, but many pre-med students extend their college career by an additional one or two years.
There is also the option of attending a post-baccalaureate (Post-bacc) program after graduation. A post-bacc is designed for any student looking to fulfill course requirements for their B.S. degree or earn a second B.S. degree. The majority of post-bacc attendees are pre-med students who need to complete the prerequisite course requirements.
MEDICAL SCHOOL: 4 YEARS
So exactly how long is medical school? In total 4 years. Once you’ve made it to med school, you’ll begin two years of pre-clinical work, which essentially is an extension of your pre-med course requirements. During this period, students are also required to take the United States Medical Licensing Examination® (USMLE®) Step 1 exam. USMLE, is a series of examinations that are taken throughout med school to ensure students are developing the skills they’ll need to become a doctor.
Clinical work begins in the third year of med school and gives students a chance to get hands-on experience as a doctor. Students shadow physicians in a hospital or clinical setting and work with patients under supervision.
By the end of the third year of med school, it’s time to decide what kind of doctor you want to be, as you’ll take elective courses in your chosen specialty during your final year. Students also typically take the USMLE Step 2 exam in their last year of med school.
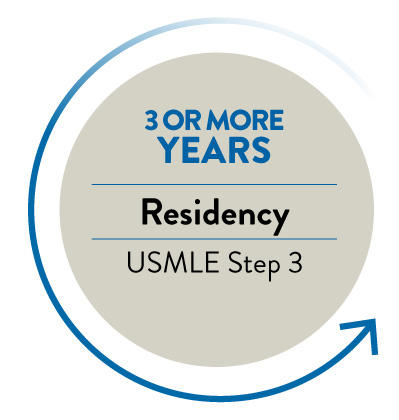
RESIDENCY: 3+ YEARS
Now that you know exactly how long is medical school, the next step in the journey to becoming a physician is completing residency. After successful completion of med school, graduates have obtained a training certificate and are assigned to a residency program. A residency, or internship, is a position at a teaching hospital in which you perform your duties as a doctor under supervision. Residency length varies by specialty, from three years for general internal medicine to seven years for neurosurgery.
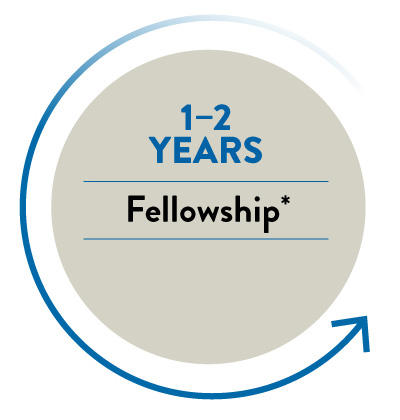
For specialties such as radiology, anesthesiology, and dermatology, interns must complete one year of generalized training, called a transitional or preliminary year, before starting a residency in their specialty. And some medical subspecialties require additional training through fellowships, which doctors begin after completing their residency.
After the first year of residency, interns take the USMLE Step 3, the final exam in the series before you receive your medical license.
LICENSING
You now know precisely how long is med school and the education that follows, but there is one last step. Once you’ve successfully completed all of the training required to achieve your medical license, you can begin practicing independently as a licensed physician.
You’ve made it to the finish line, but you’ll still need to keep up with Continuing Medical Education in order to continue practicing as a physician in some states or medical settings. This ensures that you stay educated and up to date on the latest research and best medical practices.
Now that you have the answers to the questions: how many years is medical school? How long does medical school take? And you have a better understanding of the medical school timeline, it’s time to dive into researching which medical schools might be the right fit for you. You can begin by reading about how American University of the Caribbean School of Medicine’s M.D. Program helps prepare future doctors to be leaders in their chosen field.
Related resources: