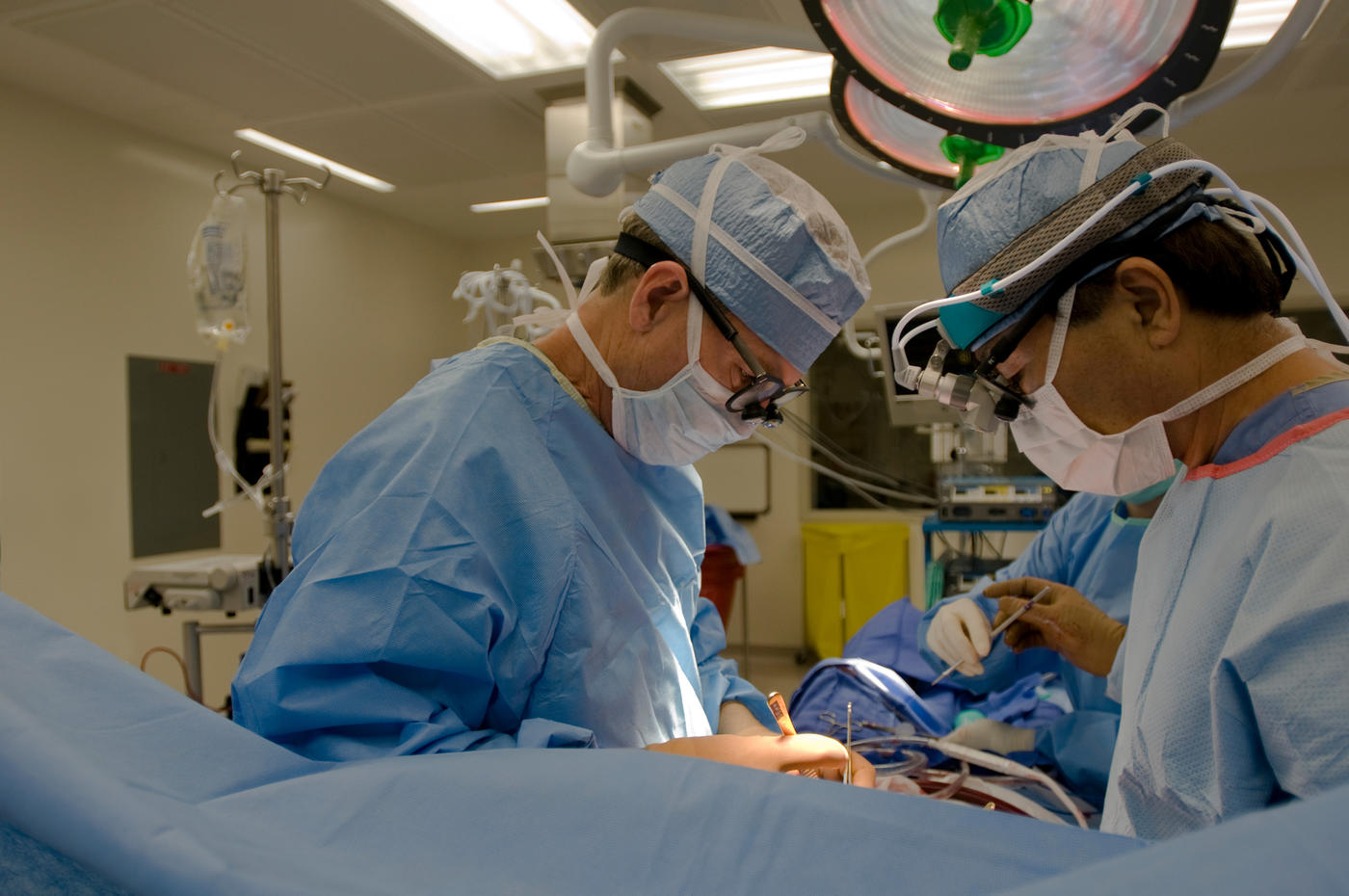
You’re interested in becoming a physician, and you are drawn to surgery as a topic of study. You know that all physicians receive some surgery training and are qualified to perform basic operations. You are also aware that there are different types of surgical specialists—neurological surgeons, for example, treat disorders of the brain, spinal cord, and associated nerves; cardio and thoracic surgeons specialize in treating the heart and lungs. But which type of surgery intrigues you most? If your interests fall into several categories, you may consider becoming a general surgeon.
What is a general surgeon? What does a general surgeon do? Whereas surgical specialists focus on a particular organ or region of the body, general surgeons are experts in common surgeries such as splenectomies (spleen removal) and appendectomies (removal of the appendix). Their broad training and surgical knowledge gives them an advantage when dealing with issues affecting multiple organs and systems of the body. Read on to learn more about the road to becoming a general surgeon.
Steps to Becoming a General Surgeon
What is a General Surgeon?
Surgeons perform operations to treat deformities, disease, and injuries. Surgeons must be highly skilled in the use of surgical tools and possess a great deal of scientific knowledge. The American College of Surgeons (ACS), a professional association that sets standards for surgical education and practice, says that all surgeons must learn the following topics, which they consider to be core knowledge:
- Anatomy
- Immunology
- Intensive care
- Metabolism
- Neoplasia
- Nutrition
- Pathology
- Physiology
- Shock and resuscitation
- Wound healing
General surgeons use their training and knowledge to treat conditions affecting nearly every area of the body. Their specialized knowledge lies in the diagnosis of patients and providing care before, during, and after operations, including the management of surgical complications. General surgeons must use that knowledge to address issues regarding the nine primary components of surgery as defined by the ACS:
- Abdomen
- Alimentary tract
- Breast, skin, and soft tissue
- Critical care
- Endocrine system
- Head and neck
- Surgical oncology
- Trauma care
- Vascular system
As you can see, general surgeons are knowledgeable in many surgical techniques and areas of study. This gives them the ability to deal with a wide variety of cases in the operating room. But what training is involved in learning how to address such a broad field of study? Read on to learn how to become a general surgeon.
General Surgeon Education Requirements
The first step toward becoming a general surgeon is to become a medical doctor by graduating from an accredited medical school, such as the American University of the Caribbean School of Medicine (AUC)*. AUC is located on the Caribbean island of St. Maarten. Students at AUC take two years of medical science classes followed by two years of clinical training, just like students at United States-based medical schools.
AUC’s medical sciences curriculum is completed on campus in St. Maarten, while the clinical portion of one’s training can be completed at AUC’s affiliated clinical hospitals in the United States and the United Kingdom. AUC also partners with the University of Central Lancashire (UCLan) for a UK track option. The first two years of which focus on studying the medical sciences, through the delivery of a Post Graduate Diploma in International Medical Sciences from UCLan, which AUC recognizes as equivalent to its own medical sciences curriculum, and the final two years completing clinical clerkships across AUC’s network of affiliated teaching hospitals.
Clinical training consists of rotations (also known as clerkships) in a variety of medical disciplines including internal medicine, surgery, and pediatrics. Following the core clerkships, medical students choose elective clerkships in subspecialties that will provide them with the knowledge and skills necessary for the next step in the process: postgraduate residency.
Residencies give newly degreed doctors the opportunity to practice and hone their skills before they are licensed to practice medicine. The ACS sets the standards for the study of general surgery. General surgery residencies last at least five years, at least 54 months (4.5 years) of which must be devoted to the study of clinical surgery, including emergency care, endoscopy, and intensive care. At least three of those years must be devoted to the primary components of surgery. In addition, no more than one year can be devoted to the study of a particular surgical discipline other than those considered primary components of surgery, and no more than six months can be devoted to topics in nonclinical surgery.
AUC’s Office of Career Advisement can help guide students through the process of choosing which residency programs meet their interests and then applying to them through the National Resident Matching Program® (NRMP®). This placement system helps pair medical students who wish to become licensed in the U.S. with residency programs. In 2021, AUC students attained residencies in 17 medical specialties in programs in 39 U.S. states and territories. Of those, students attained general surgery residencies at such hospitals as Ascension St. Agnes Hospital in Maryland; Flushing Hospital Medical Center in New York; Riverside Community Hospital in California; and The University of Illinois at Chicago.
After completing their general surgery training, doctors can apply for fellowship (membership) in the ACS and for certification by the American Board of Surgery. These organizations can help doctors network with other physicians, find additional educational opportunities, and learn about developing topics in the surgical sciences.
Now that you know what general surgeons are, what they do, and how they are trained, apply to AUC and get started on your road to becoming a general surgeon.
Related resources:
- Types of Surgeons: What Field of Surgery is Right For You?
- Fellowship of the American College of Surgeons: General Surgery
- AUC Curriculum For MD Program in Caribbean
*American University of the Caribbean School of Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Commission on Colleges of Medicine (ACCM, www.accredmed.org), which is the accreditor used by the country of St. Maarten.